VIEW ALL
BEV
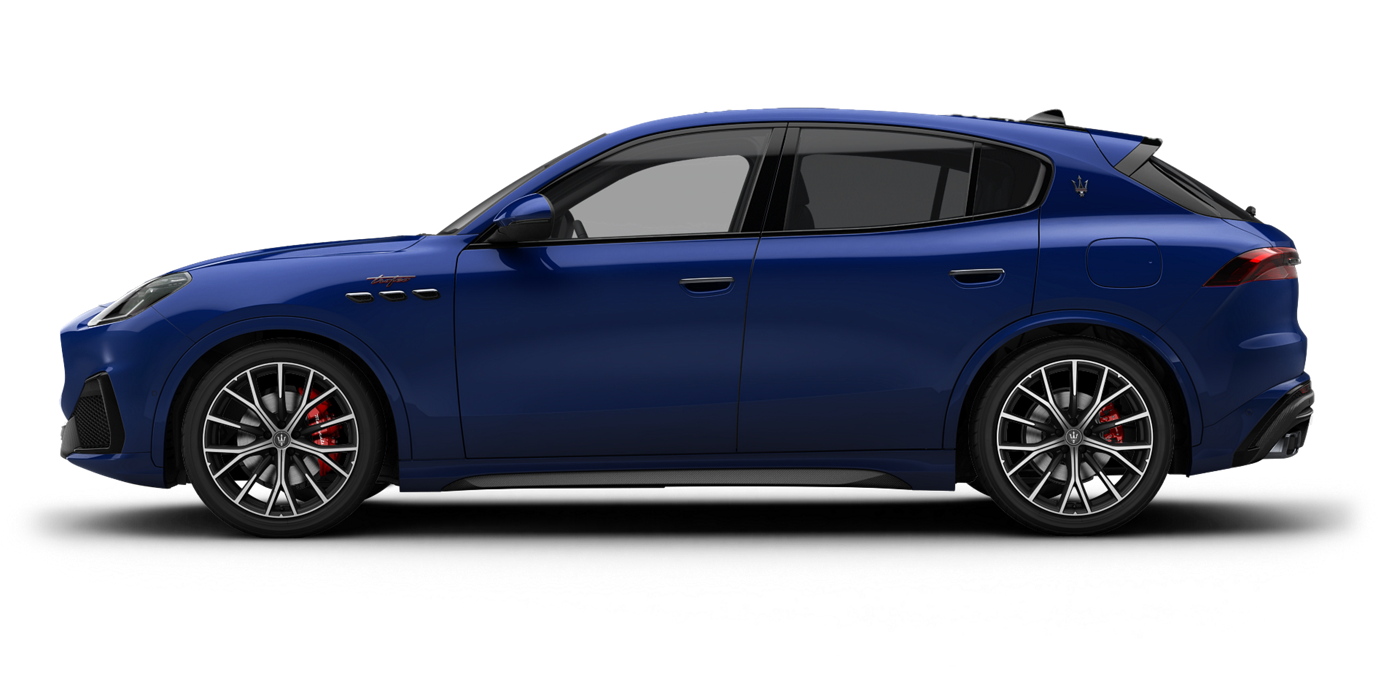
Grecale
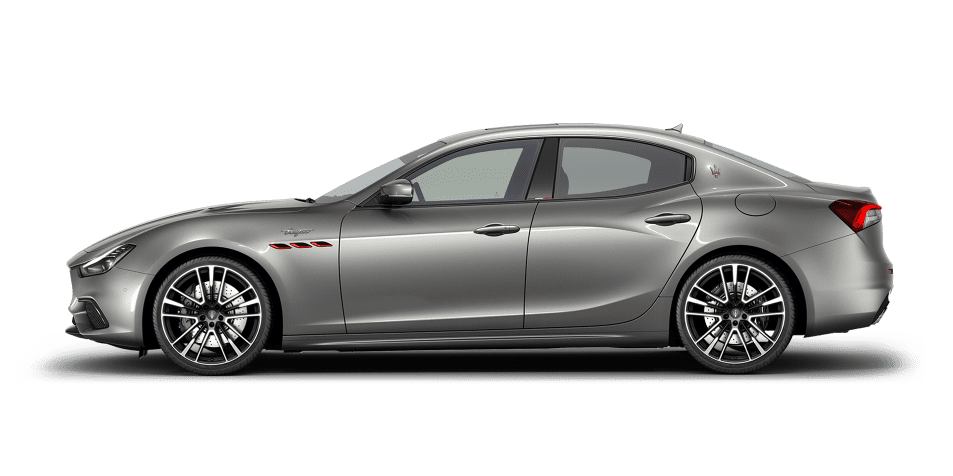
Ghibli
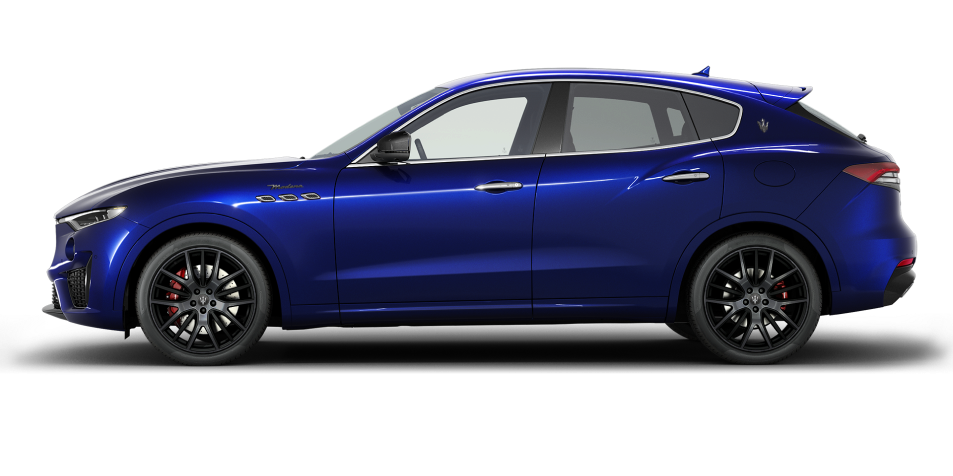
Levante
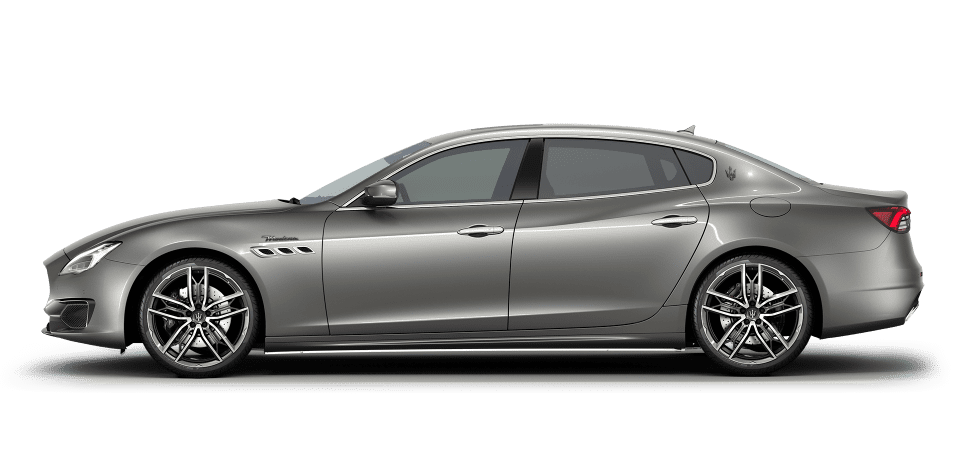
Quattroporte
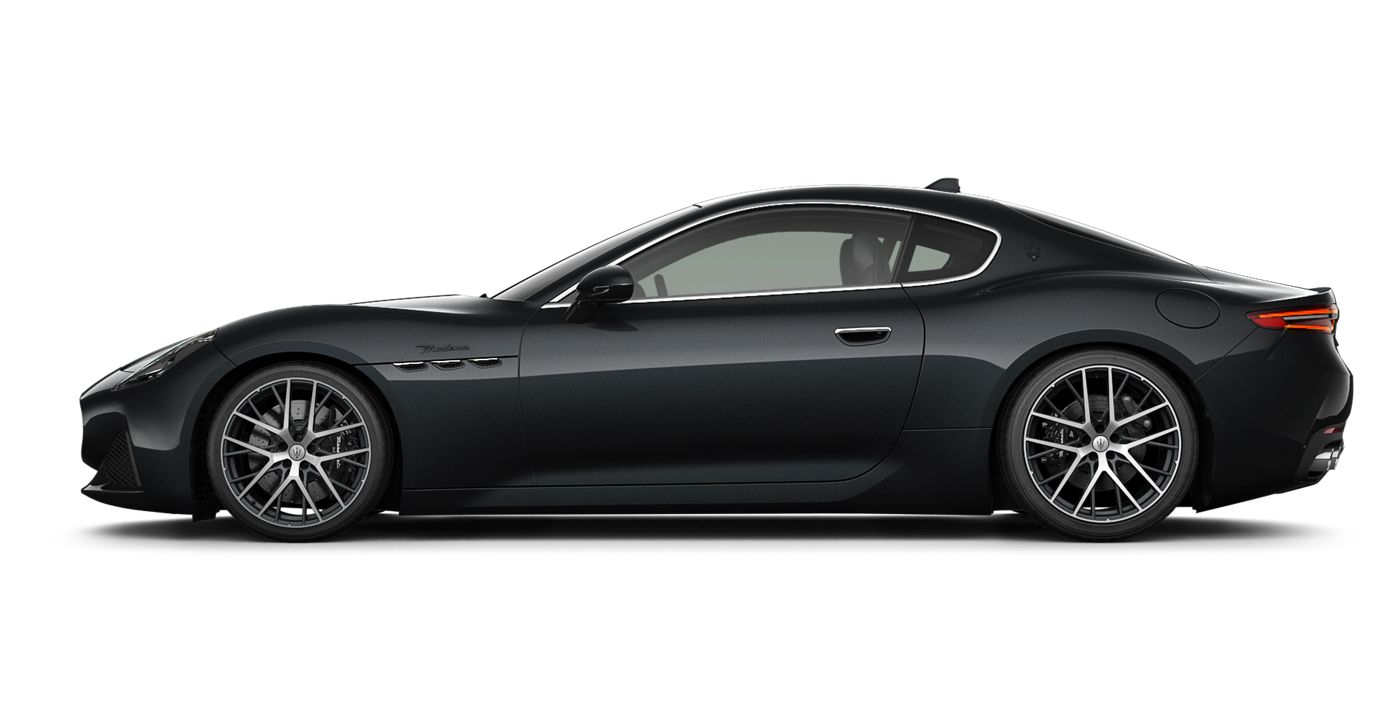
GranTurismo
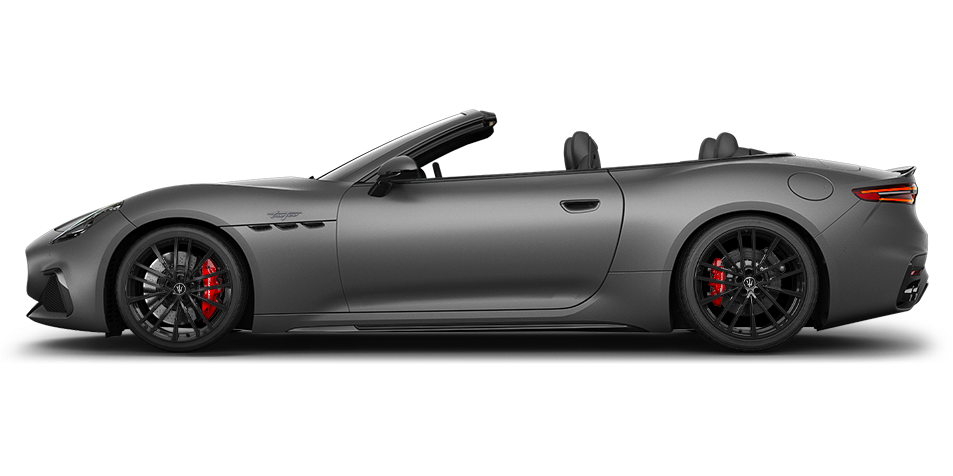
GranCabrio
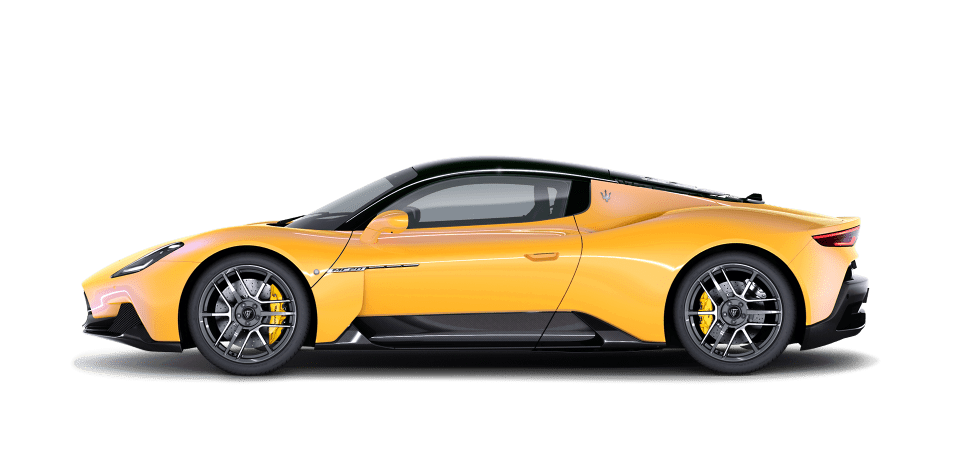
MC20
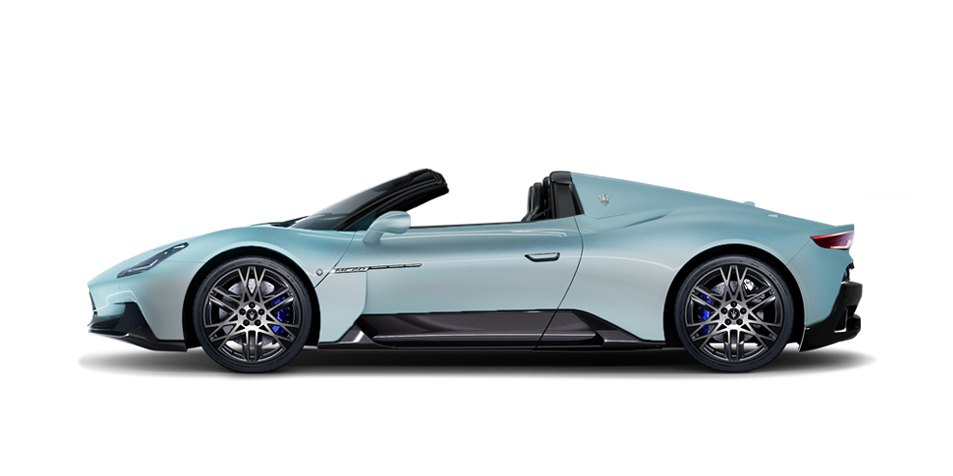
MC20 Cielo
Folgore
Fuoriserie
Special Series
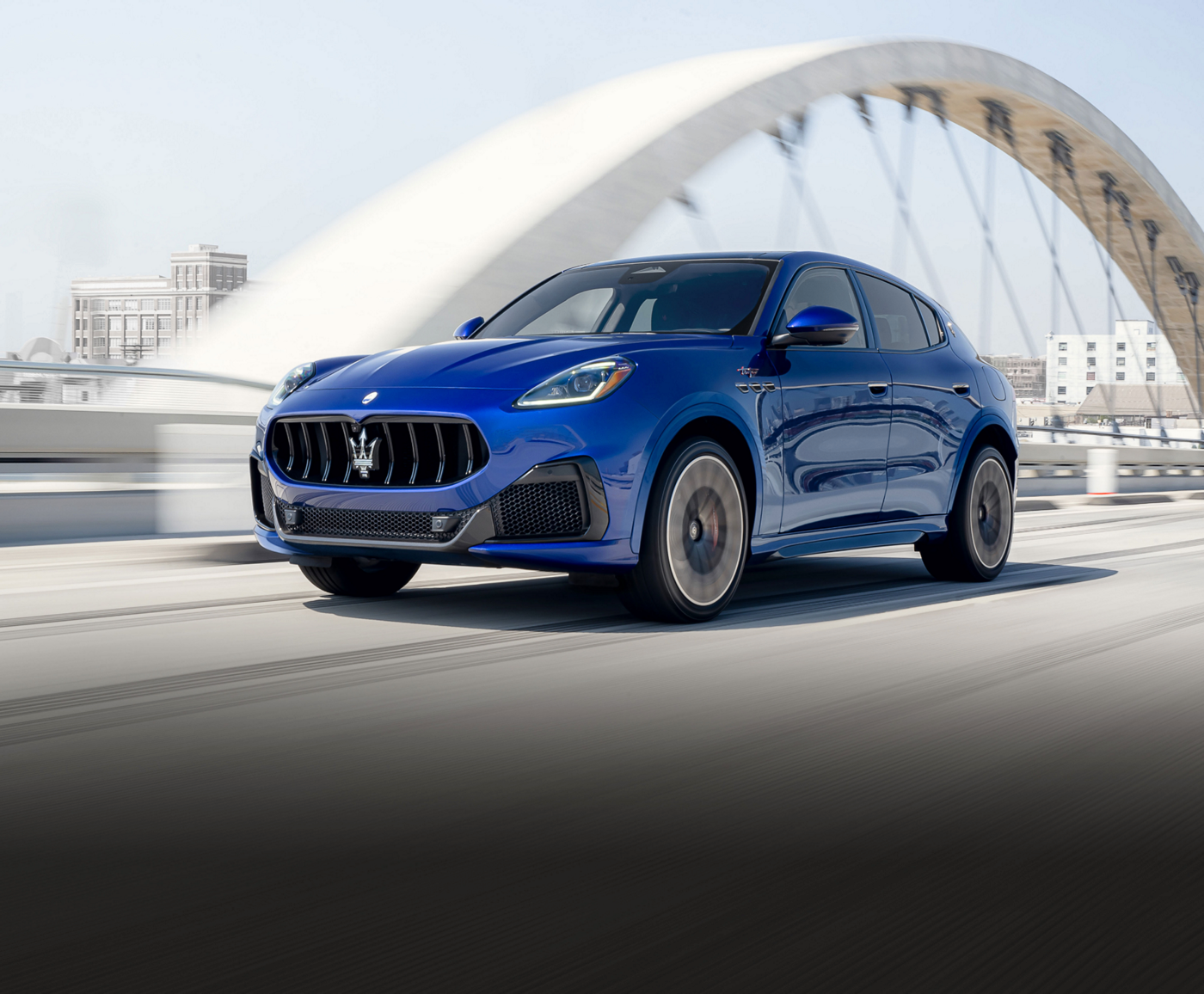

Everyday Exceptional
Top Speed
Acceleration
Acceleration
Power
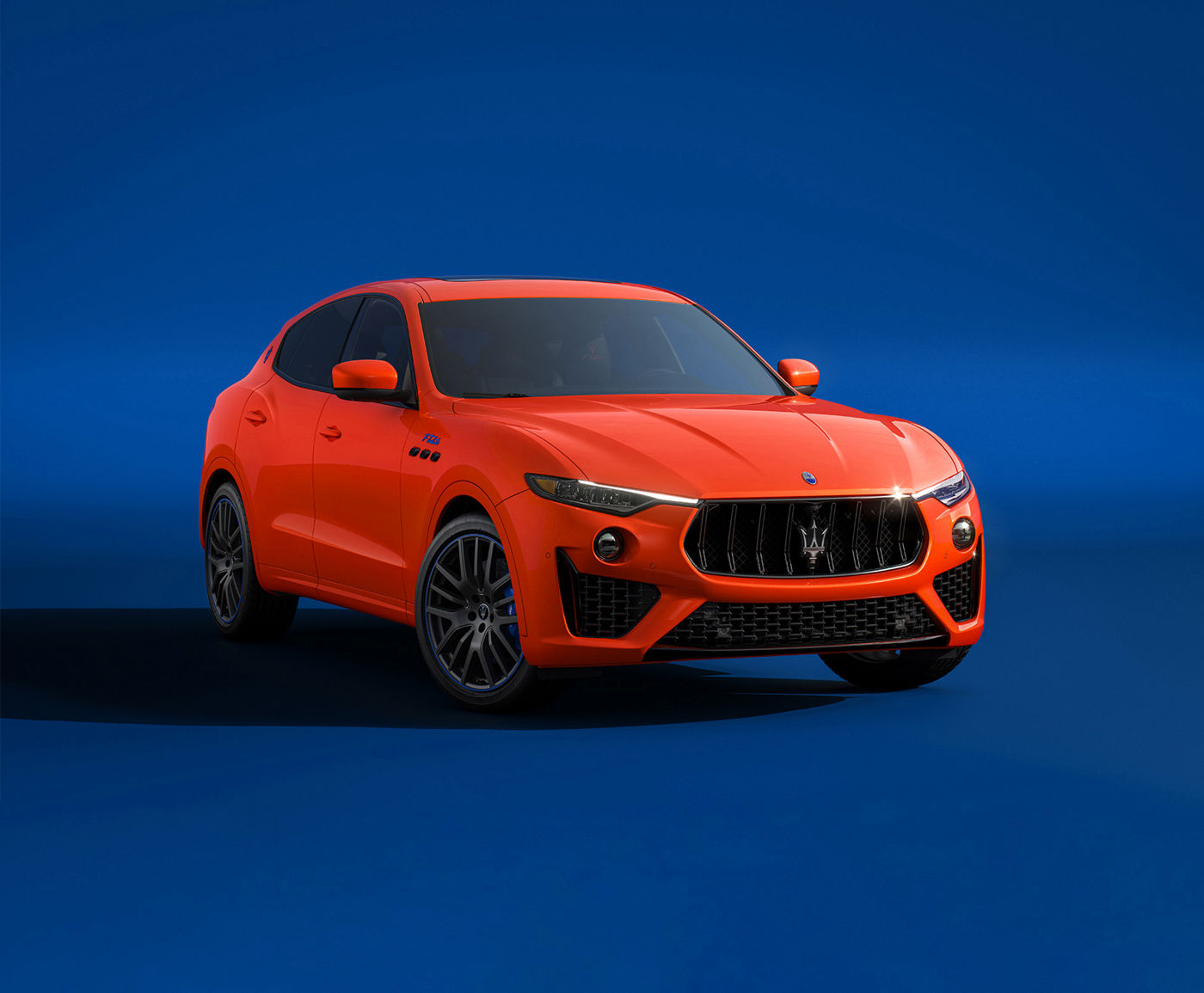




You're Not Like Everyone Else
From
$133,500
Top Speed
Acceleration
Acceleration
Power
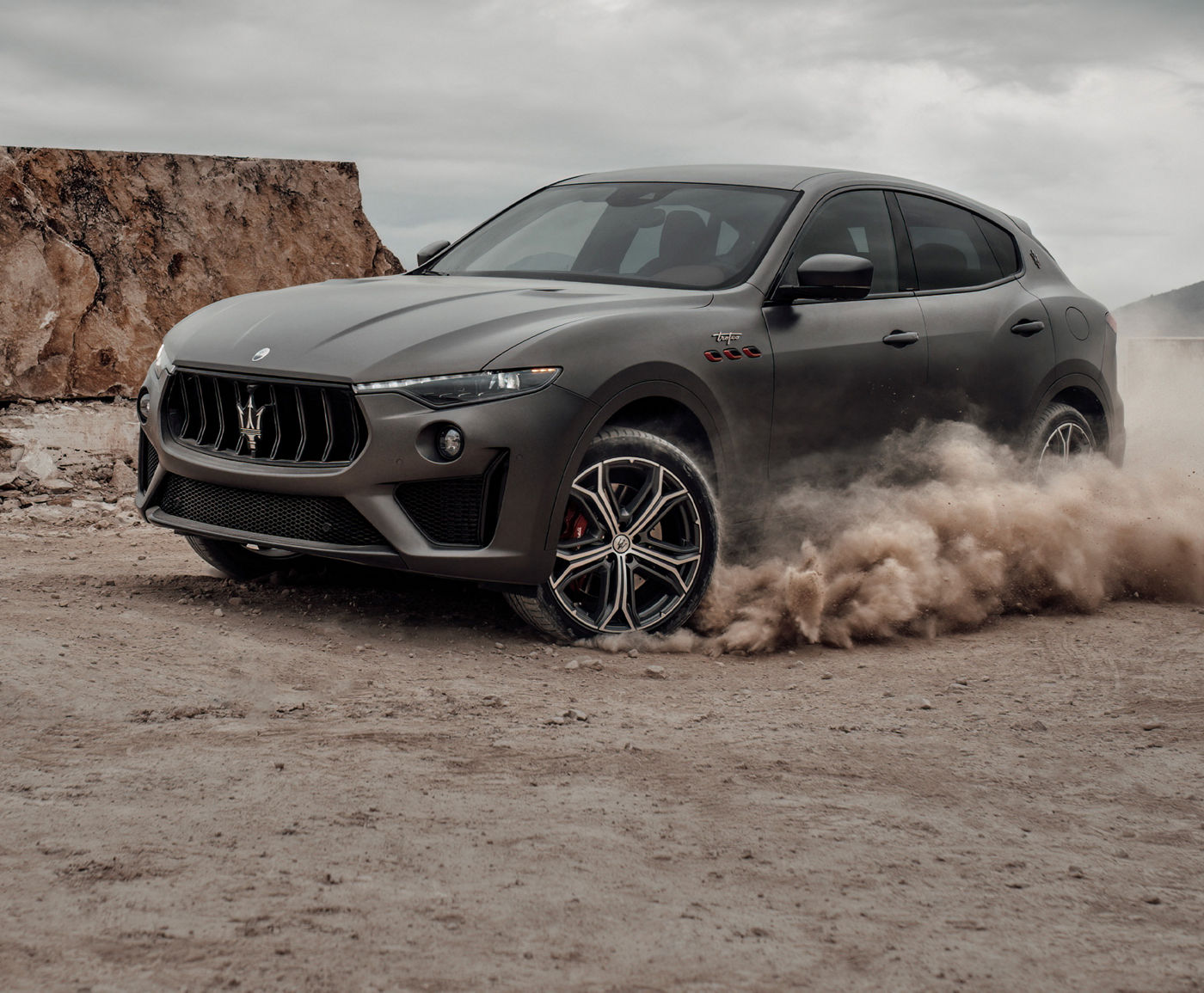




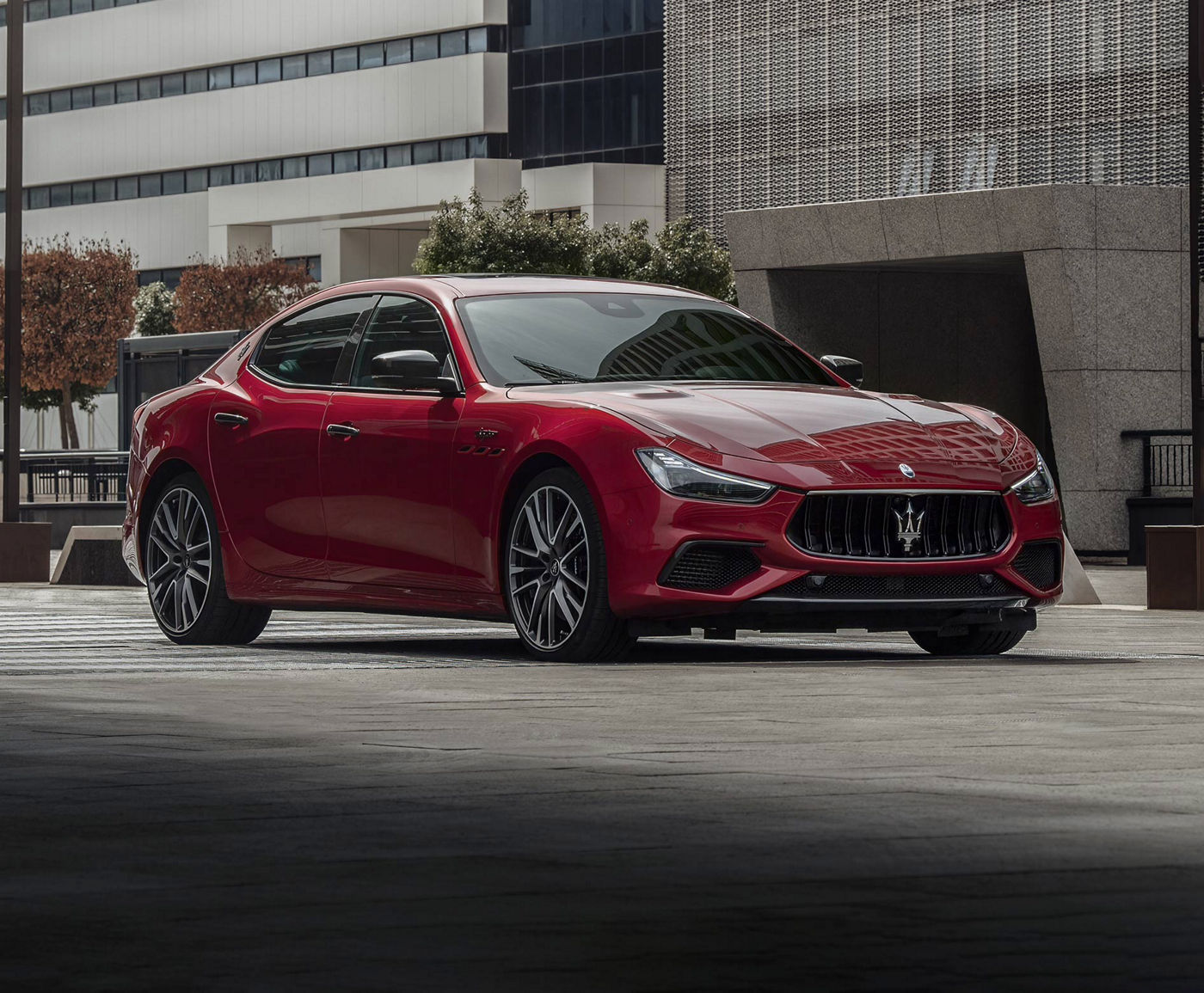
The Maserati of SUVs
Top Speed
Acceleration
Acceleration
Power
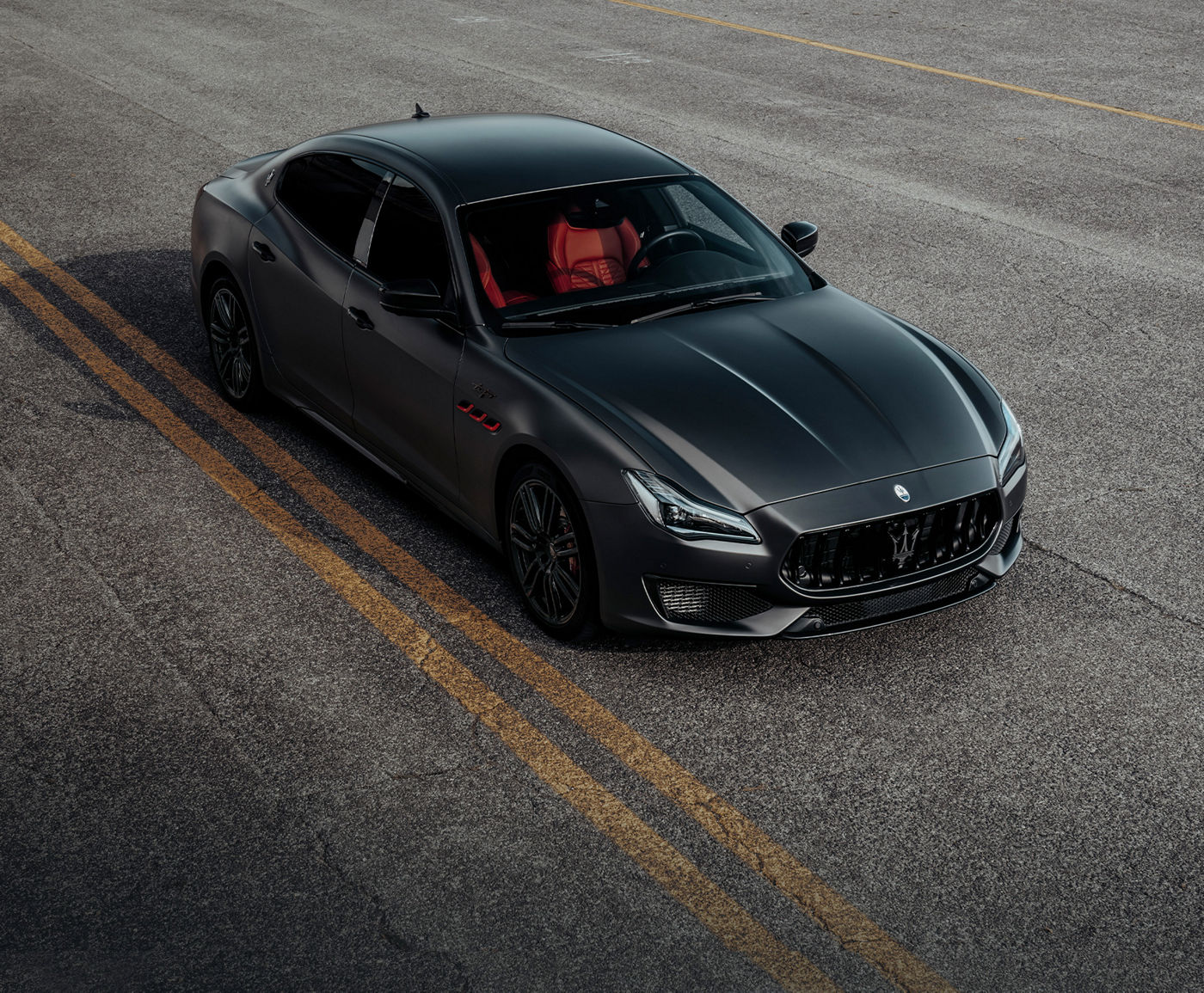




An Icon of Italian Elegance
Top Speed
Acceleration
Acceleration
Power
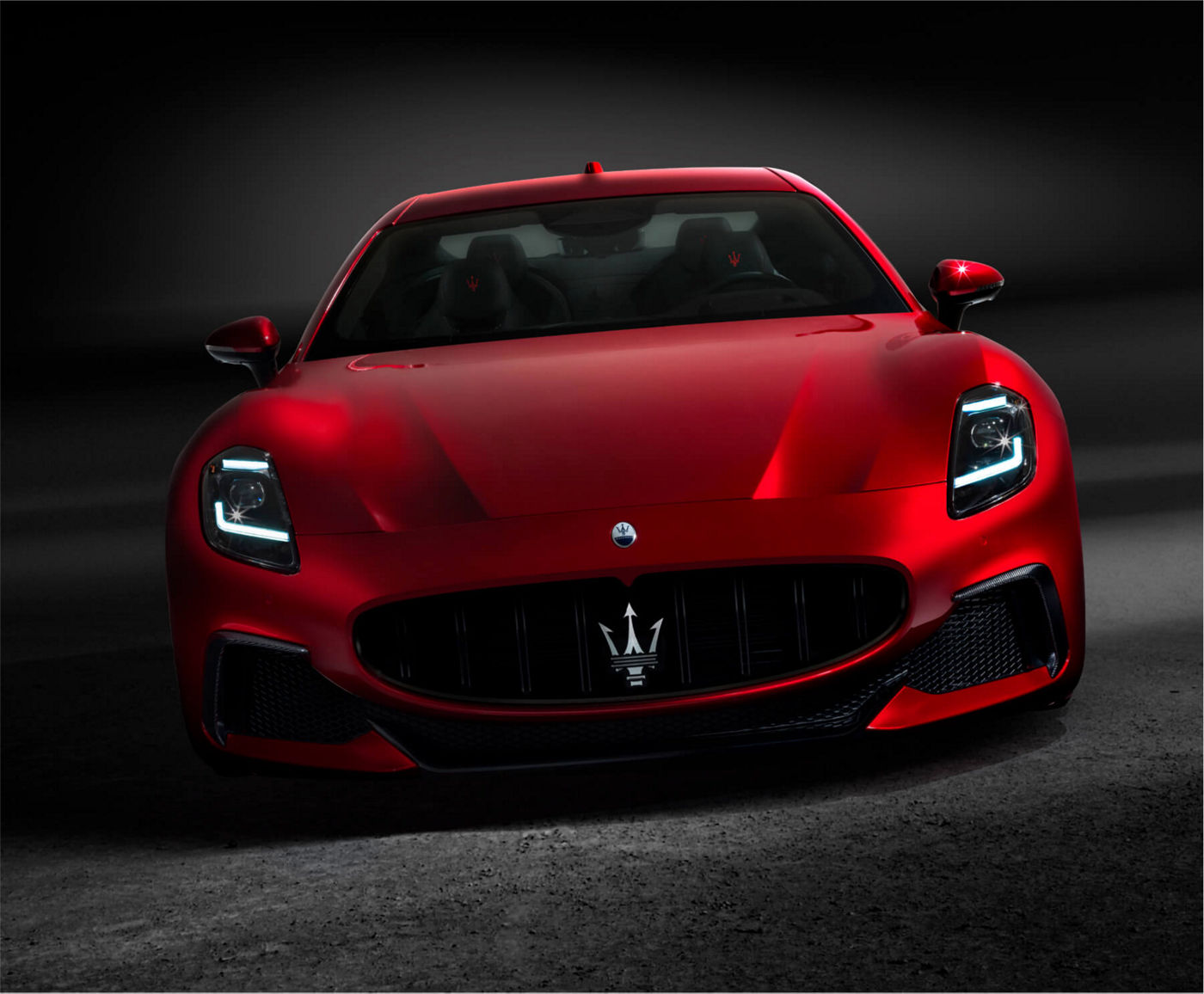




The others just travel
Top Speed
Acceleration
Acceleration
Power
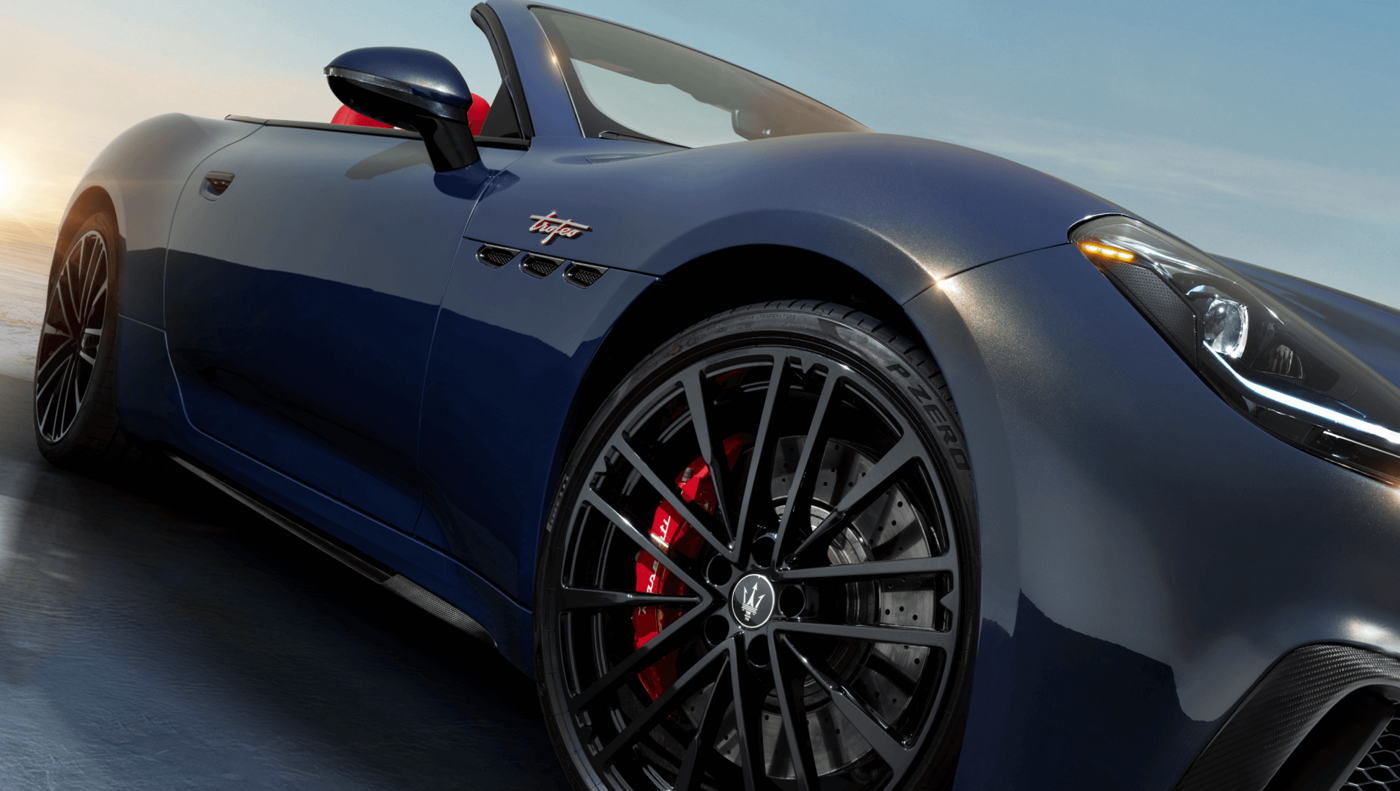




Drive Like the Best Is Yet to Come
European metrics shown. Please stay tuned for updates using the Keep in Touch Form.
Top Speed
Acceleration
Acceleration
Power
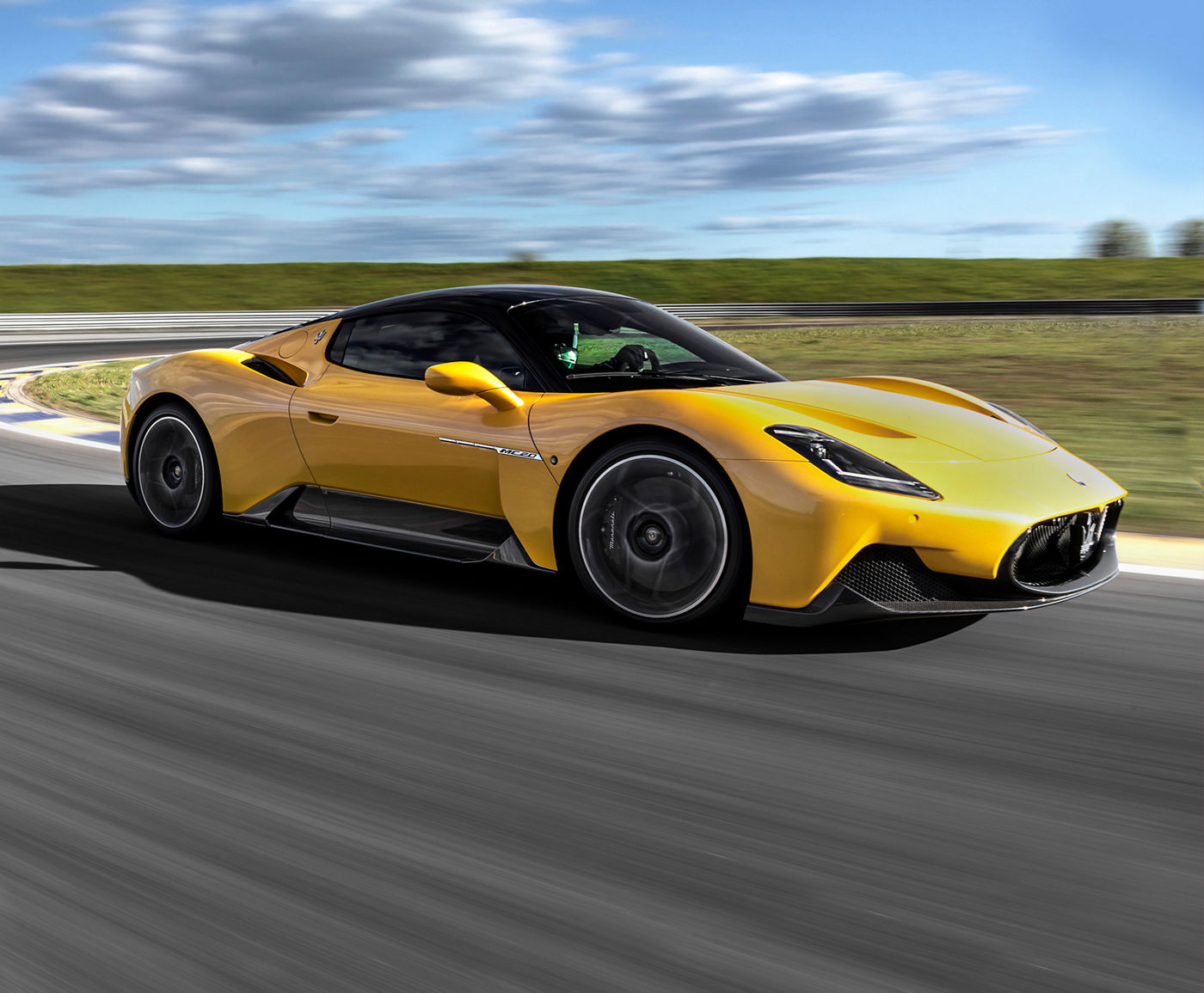




The First of Its Kind
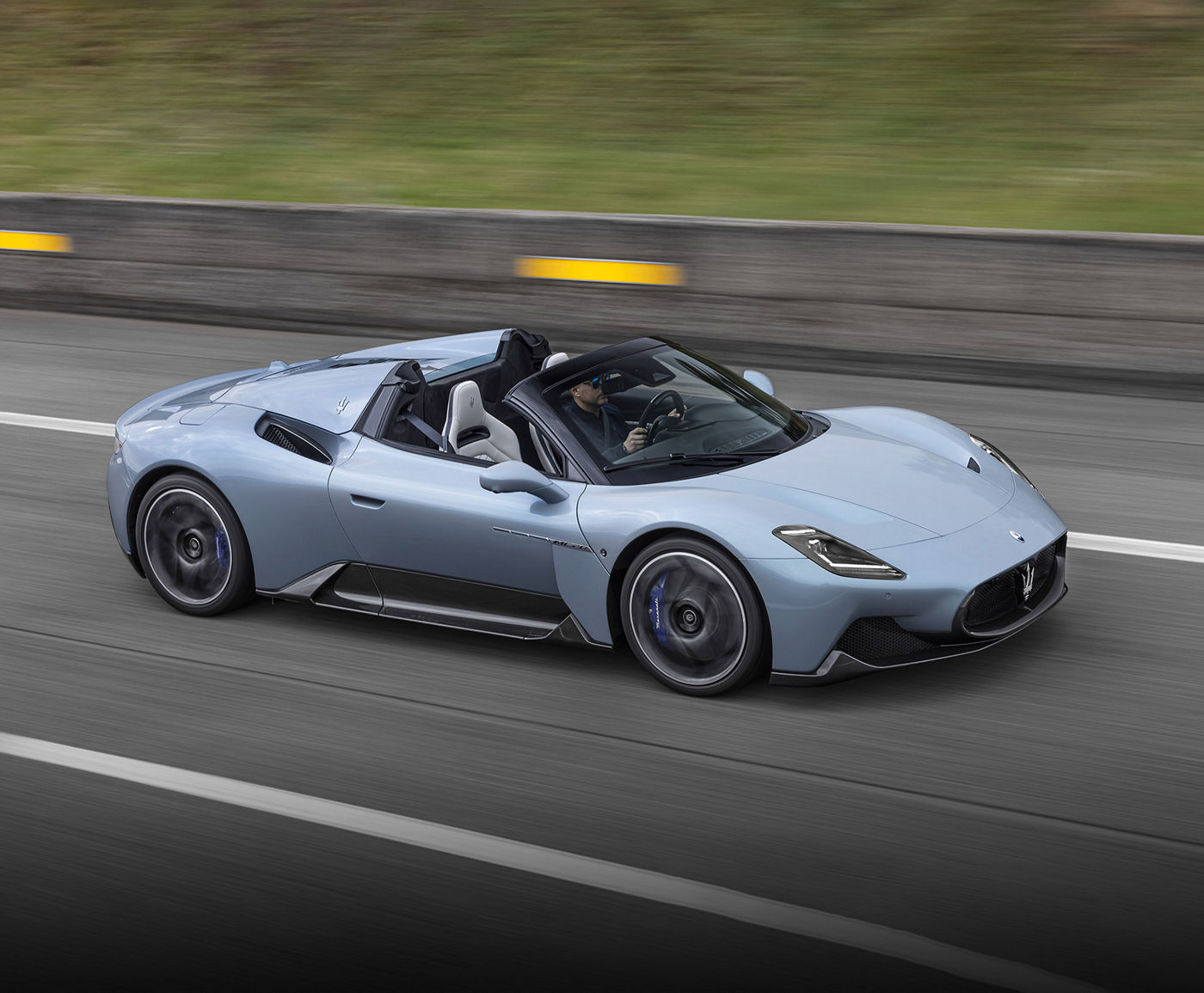




Beyond the Sky
Top Speed
Acceleration
Acceleration
Power



History
Events
Stories of Audacity
Maserati Tridente
Fuoriserie
Corse
Legacy
Experiences
Store
Partners
Values











Maserati Connect
Maserati Heritage
Service and Assistance
Customization
Maserati Club
Certified Pre Owned
Current Offers
Shop Grecale
Shop Levante
Shop GranTurismo
Search New Inventory